Vol 1, No 1 (2025): Volume 1, Issue 1, 2025
Original Article
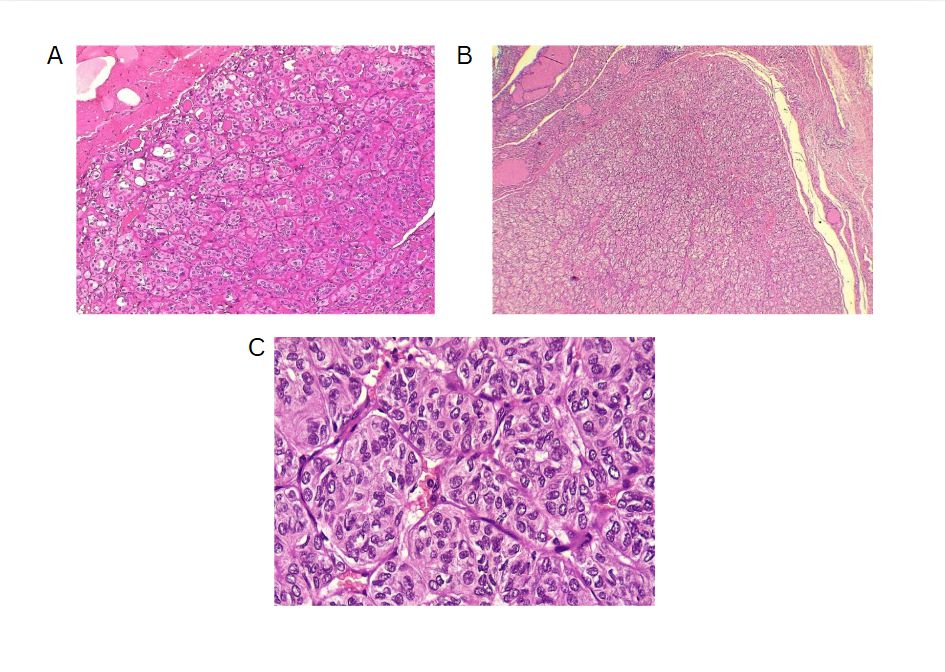
Hyalinizing Trabecular Tumor: A Case Series with Literature Review
Abdulwahid M. Salih, Rebaz O. Mohammed, Hiwa O. Baba, Shko H. Hassan, Muhammed Bag A. Ali, Imad...
Introduction: Hyalinizing trabecular tumor (HTT) is a rare thyroid neoplasm originating from follicular cells and poses diagnostic challenges due to its cytologic and histologic overlap with other thyroid malignancies. This study aims to present the clinical features and management of HTT cases treated at a single center.
Methods: This was a single-center retrospective case series. The patients were included from January 2019 to November 2024. Data collection took place over one month, from November 15, 2024, to December 15, 2024. The study included patients with HTT whose diagnoses were confirmed histopathologically.
Results: The case series included 11 patients, predominantly female, 10 (90.9%), with a mean age of 50.7±19.01 years. The most common presenting symptom was anterior neck swelling, recorded in 5 (45.5%), while one case (9.1%) was discovered incidentally. Hyperthyroidism was present in 6 (54.5%). The tumors were distributed within the thyroid gland as follows: left lobe in 5 (45.5%) cases, right lobe in 4 (36.4%) cases, and isthmus in 2 (18.1%) cases. Total thyroidectomy was performed in 7 patients (63.6%), with tumor sizes ranging from 0.5 to 5.5 cm and a mean diameter of 2.6 ± 2.05 cm. All diagnoses were confirmed postoperatively through histopathological examination.
Conclusion: A rare benign tumor, HTT remains challenging to diagnose accurately. Both total thyroidectomy and lobectomy may result in good outcomes.
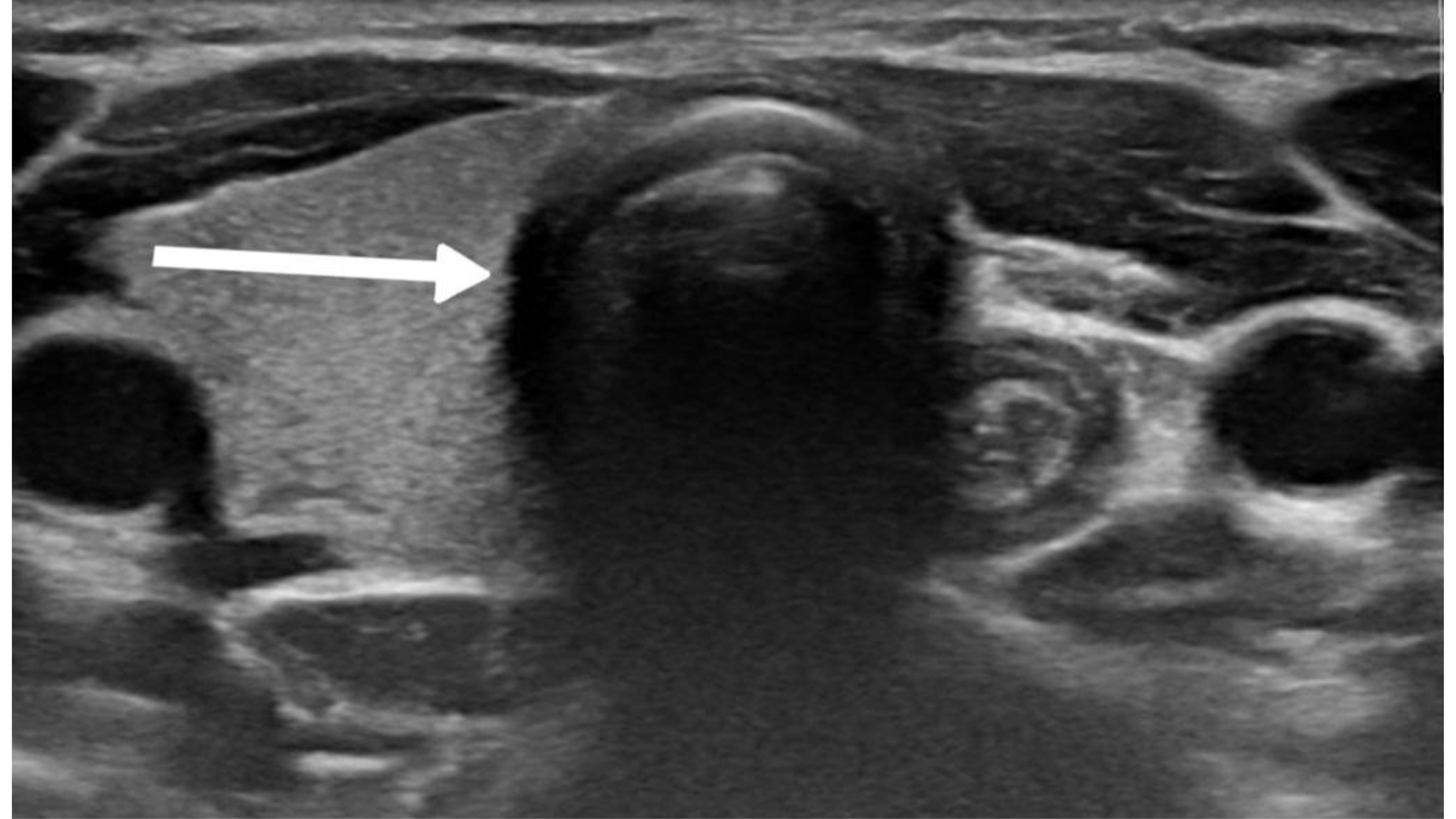
Thyroid Hemiagenesis: A Single-Center Case Series
Abdulwahid M. Salih, Hiwa O. Baba, Shaho F. Ahmed, Karzan M. Salih, Abdullah A. Qadir, Ayman M....
Introduction: Thyroid hemiagenesis (TH) is a rare congenital anomaly characterized by the complete absence of one thyroid lobe, with or without absence of the isthmus. Its etiology remains unclear, and epidemiological data are limited. Although TH is often asymptomatic and discovered incidentally, it may pose clinical challenges when accompanied by thyroid dysfunction or structural abnormalities. This study reviews a single-center experience in diagnosing this condition and highlights its clinical significance..
Methods: This single-center case series was conducted from July 2021–July 2024, analyzing TH cases confirmed via ultrasonography. Eligible patients had complete medical records, including demographics, clinical presentation, radiological findings, and thyroid function status. Data were retrieved from electronic records and analyzed using SPSS 27.0, employing descriptive statistics to summarize means, ranges, frequencies, and percentages, ensuring a comprehensive assessment of TH clinical and epidemiological characteristics..
Results: This study analyzed 11 patients with TH (mean age: 28.12 ± 18.14 years; range: <1–55 years), seven of whom were females (63.6%). The diagnosis was incidental in six cases (54.5%), while three (27.3%) presented with neck swelling and two (18.2%) with neck pain. Thyroid function was euthyroid in seven (63.6%), hyperthyroid in two (18.2%), and hypothyroid in two (18.2%). Ultrasound examination confirmed left lobe and isthmus agenesis in eight cases (72.7%). Follow-up ranged from 4 to 48 months.
Conclusion: This study confirms the female predominance of TH, with left-lobe absence being the most common. Congenital anomalies suggest embryological links. While thyroid function is typically preserved, those with hypo- and hyperthyroidism highlight the need for individualized endocrine assessment and monitoring.
Review Articles

Current Perspectives on Cystic Echinococcosis: A Systematic Review
Hawkar A. Nasralla, Berun A. Abdalla, Hiwa O. Abdullah, Sasan M. Ahmed, Fahmi H. Kakamad, Shvan...
Introduction: Hydatidosis, a zoonotic disease caused by the larval stage of Echinococcus granulosus, is a significant public health concern with notable economic impact. It leads to morbidity and mortality worldwide, particularly in endemic regions. This study systematically reviews recent literature on cystic echinococcosis (CE) to provide updated insights into its prevalence, impact, and management.
Methods: A systematic review was conducted using PubMed to find original articles on hydatid cysts published between
September 1, 2019, and September 1, 2024. Data extracted included the first author's name, country, publication year, study type, number of cases, clinical presentation, diagnostic methods, cyst location and quantity, cyst status, treatment type and medications, follow-up details, recurrence, and mortality rates. Data were organized and qualitatively analyzed.
Results: A total of 398 articles were identified, of which 229 articles with 1,002 patients met the inclusion criteria. Spain reported the highest number of CE cases at 362 (36.13%). Asia accounted for 487 cases (48.60%), and Europe contributed 460 cases (45.91%). The liver was the most frequently affected organ, accounting for 731 cases (72.95%), followed by the lungs with 110 cases (10.98%), and the kidney with 43 cases (4.29%). The age distribution of the cases showed that 63 (6.29%) were aged between 3 and 18 years.
Conclusion: Hydatidosis remains a significant global public health concern, impacting developing and developed countries. The liver and lungs remain the primary sites of infection. Preventive strategies, including regular animal screening and enhanced public health education, are essential for controlling the spread of the disease.
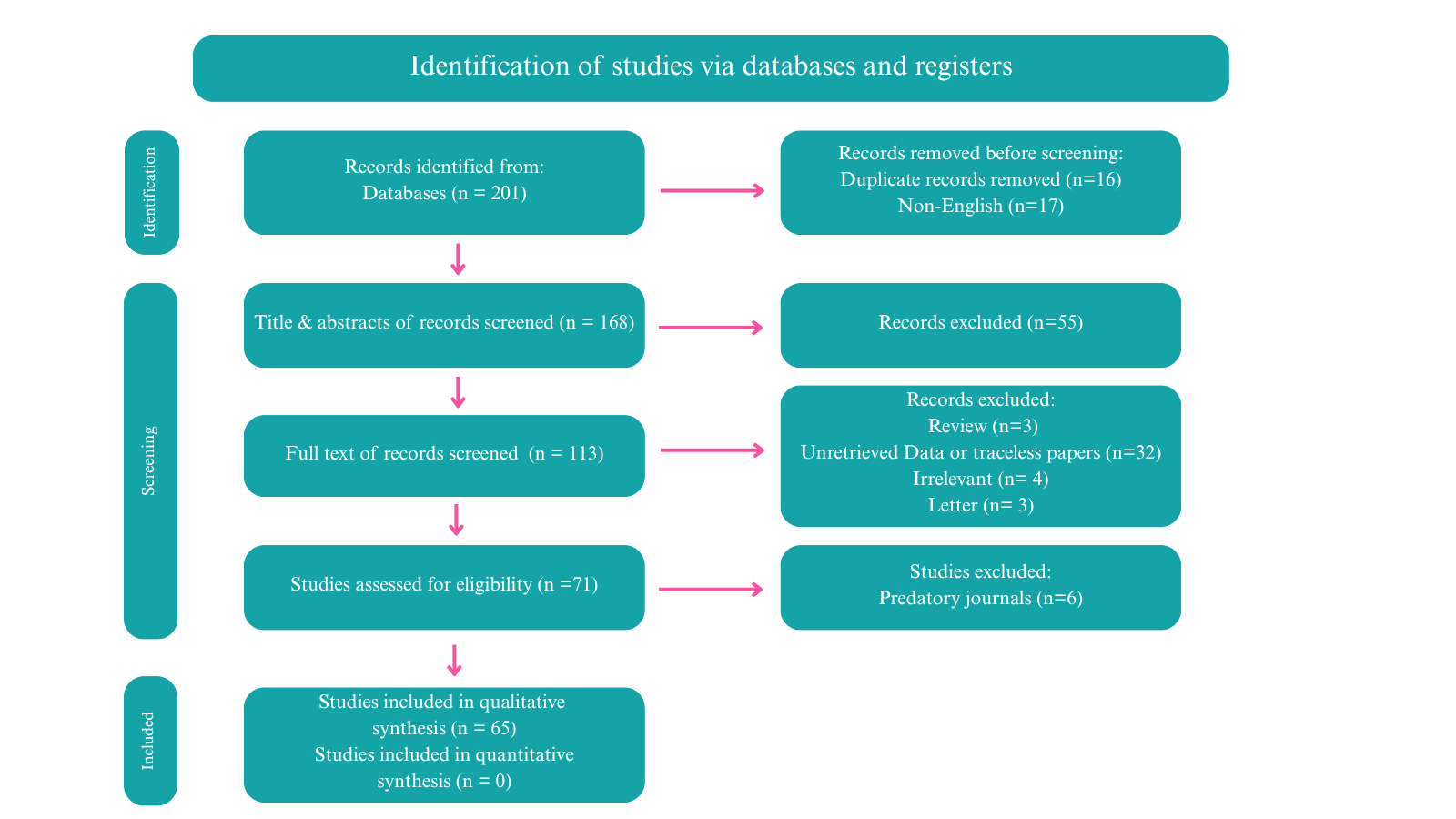
Blunt Chest Trauma and Chylothorax: A Systematic Review
Hiwa O. Abdullah, Fahmi H. Kakamad, Harem K. Ahmed, Bnar J. Hama Amin, Hadi M. Abdullah, Shvan H....
Introduction: Although traumatic chylothorax is predominantly associated with penetrating injuries, instances following blunt trauma, as a rare and challenging condition, are being increasingly documented. This study aims to systematically review the reported cases of blunt chest traumatic chylothorax (BCTC) and provide comprehensive insights into the condition.
Methods: Related studies published until December 11, 2024, were identified through Google Scholar. All studies documenting instances of BCTC, without restriction on cause or patient demographics, were included. Studies were excluded if they focused on chylothorax caused by penetrating injuries, their content was unretrievable, they were review articles, or they were published in blacklisted journals.
Results: Sixty-five eligible studies, encompassing 69 cases of BCTC, were included in the review. It predominantly affected males (73.91%), with patient ages ranging from 11 months to 84 years old. The most common clinical findings were dyspnea (47.83%) and abnormal auscultation or percussion (34.78%), with road traffic accidents as the primary cause (59.42%). Unilateral chylothorax was found in 72.46% of cases, bilateral chylothorax occurred in 27.54%, and pleural effusion was the most frequent radiological finding (55.07% in X-ray and 33.33% in computed tomography). Treatment typically included drainage (94.20%), parenteral nutrition (50.72%), and thoracic duct closure (39.13%). Most patients achieved complete recovery (89.85%), and six cases (8.70%) died.
Conclusion: The condition is rare and complex, underscored by the wide variability in patient demographics, clinical presentations, chylothorax onset, and management approaches. Given the challenges posed by limited evidence, the findings emphasize the need for early recognition and individualized management strategies.
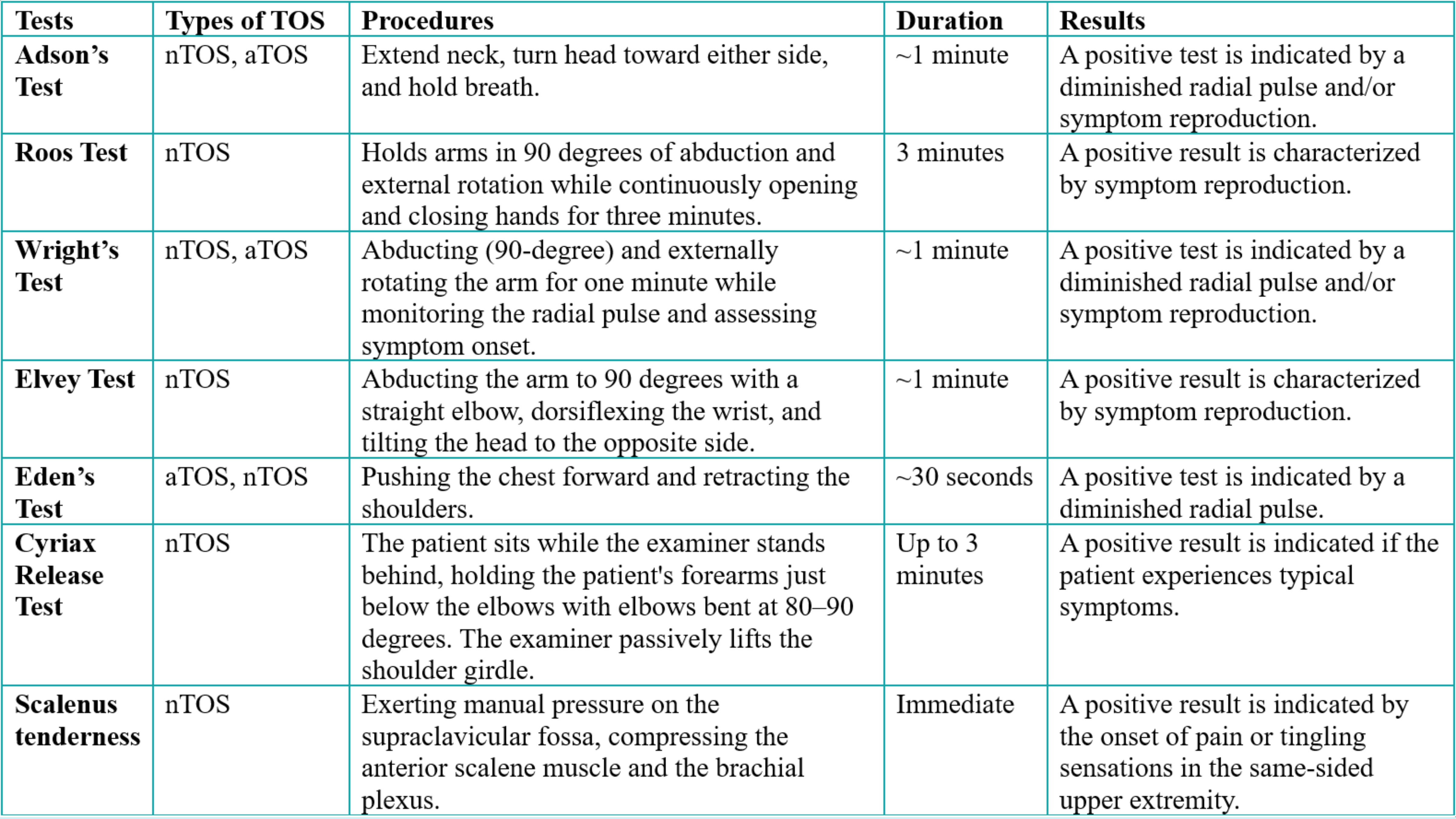
Provocative Tests in Diagnosis of Thoracic Outlet Syndrome: A Narrative Review
Fahmi H. Kakamad, Berun A. Abdalla, Saywan K. Asaad, Hawkar A. Nasralla, Abdullah K. Ghafour,...
Thoracic outlet syndrome (TOS) is a group of conditions caused by the compression of the neurovascular bundle within the thoracic outlet. It is classified into three main types based on the affected structure: neurogenic, arterial, and venous TOS. Diagnosis remains challenging due to symptom overlap with other conditions and a lack of universally accepted criteria. Provocative tests are integral to clinical evaluation, aiming to reproduce symptoms by stressing anatomical structures prone to compression. This review evaluates the commonly used provocative tests for TOS, analyzing their diagnostic performance, limitations, and clinical utility. Individual provocative tests vary widely in diagnostic performance. The Roos test demonstrates high sensitivity but poor specificity, while tests like the Cyriax Release and Wright’s hyperabduction offer better specificity at the cost of sensitivity. Most tests show significant overlap in symptom reproduction with other upper limb or cervical pathologies, contributing to high false-positive rates. Combining multiple tests improves diagnostic accuracy but still falls short of a definitive standard. While provocative tests are valuable for screening and clinical assessment of TOS, their standalone diagnostic reliability is limited. A multimodal approach integrating clinical examination, imaging, and electrodiagnostic studies is essential for improving diagnostic confidence and patient outcomes. Future research should aim to standardize testing protocols and validate findings through large-scale, population-based studies.
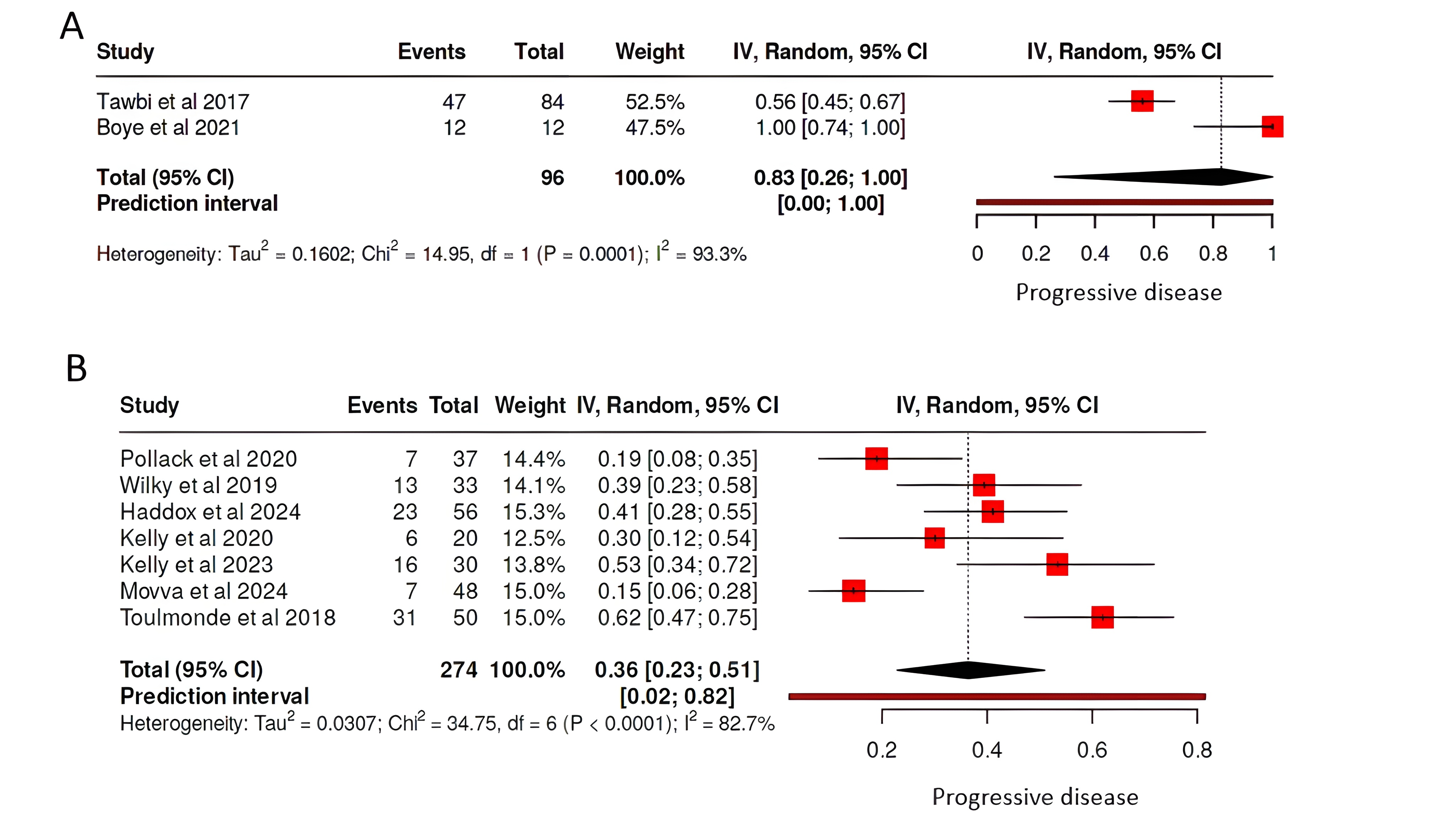
Pembrolizumab and Sarcoma: A meta-analysis
Rebaz M. Ali, Sami S. Omar, Shalaw H. Abdalla, Fattah H. Fattah, Shnya R. Hamalaw, Hussein M....
Introduction: Pembrolizumab is a monoclonal antibody that promotes antitumor immunity. This study presents a systematic review and meta-analysis of the efficacy and safety profile of this treatment as monotherapy or in combination with other drugs for the treatment of sarcomas.
Methods: A literature search was conducted across Google Scholar, PubMed/MEDLINE, and EMBASE from February 15th to April 15th. Eligible studies were clinical trials that reported efficacy or outcomes of pembrolizumab in sarcoma patients, either alone or in combination with other drugs. In contrast, those lacking sufficient data or not meeting trial criteria were excluded.
Results: Ten clinical trials met the eligibility criteria, including 419 sarcoma patients (53.7% male; median age 55.4). Pembrolizumab was administered either as monotherapy in 23% of cases or in combination with other agents in 77% of cases. The progressive disease rate was 83% with monotherapy and 36% with combination therapy. Objective response rates varied, with the highest observed in the pembrolizumab plus talimogene laherparepvec combination (35%) and the lowest in pembrolizumab monotherapy (ranging from 0% to 11.2%). Median progression-free survival ranged from 1.4 (Pembrolizumab + Cyclophosphamide) to 7.8 months (Pembrolizumab + Lenvatinib in undifferentiated pleomorphic sarcoma). Combination therapy was associated with significantly better tumor response (<0.001). However, rates of endocrine, gastrointestinal, some hepatic, and dermatological adverse events were significantly associated with combination therapy compared to monotherapy (p < 0.05).
Conclusion: Pembrolizumab-based combination therapies have the potential to enhance treatment efficacy in sarcoma, although they may be associated with an increased risk of adverse events.
Case Reports
Pediatric Adrenal Hydatid Cyst: A Case Report and Literature Review
Wirya N. Sabir, Hadeel A. Yasseen, Shwan F. Abdulaziz, Paiwand A. Nadr, Shaho F. Ahmed, Meer M....
Introduction: Echinococcosis is a zoonotic disease that can affect various organs and tissues in the human body. However, primary adrenal hydatid cyst (AHC) is rare and may be overlooked, making its early detection crucial. This report presents a case of an incidentally diagnosed primary AHC.
Case presentation: A 5-year-old female with an unremarkable medical history underwent abdominal ultrasonography for assessment of an inguinal hernia, and a right adrenal lesion was incidentally discovered. Intraoperatively, the lesion was suspected to be AHC, which was later confirmed by histopathology.
Literature review: The 10 cases of AHC that were reviewed had a mean age of 46.2 ± 12.2 years; six patients were male. Three cases had a history of contact with animals. No laterality differences were observed, and the mean cyst size was 7.45 ± 2.7 cm. Flank pain was the most common symptom (3 of 10), and surgery was performed for all the cases, accompanied by antiparasitic drugs in five cases. No cases of recurrence were reported.
Conclusion: Primary AHC can be easily overlooked or misdiagnosed as an adrenal mass, often being identified incidentally during investigations for unrelated health concerns. Surgical excision of the cyst without rupture may yield favorable results.
Multiple Concurrent Pilonidal Sinuses: Case report and Literature review
Emad S. Siddiq, Shko H. Hassan, Abdullah A. Qadir, Meer M. Abdulkarim, Ibrahim H. Qader, Khalis...
Introduction: Concurrent pilonidal sinuses (PNSs) at distinct locations are extremely rare. This report highlights an exceptional case of a young female presenting with three PNSs in distinct locations.
Case presentation: A 19-year-old female with a family history of PNS presented with a chronic, discharging sinus tract in the intermammary region that had persisted for two years. Physical examination revealed an erythematous lesion with intermittent purulent and bloody discharge, leading to a diagnosis of intermammary PNS (IMPNS). Surgical excision was performed, and histopathology confirmed the diagnosis. Six weeks postoperatively, the patient’s wound had completely healed; however, she mentioned symptoms in the umbilical and sacrococcyx regions that had been intermittent for the past year. Further evaluation led to diagnoses of natal cleft PNS (NCPNS) and umbilical PNS (UPNS). NCPNS was scheduled for surgical treatment, while UPNS was managed conservatively. Histopathology confirmed chronic sinus tract formation in both cases.
Literatue review: Nine cases of PNS were reviewed, six of which were males. Two of them had recurrent discharging sinuses, and no family history of PNS was reported. Locations included gluteal, auricular, mammary, cheeks, and umbilical regions. Discharge was present in all of the cases, accompanied by pain in two. Sinus excision was performed for all the cases, accompanied by laser epilation in one. Healing modalities included secondary intention and various dressings.
Conclusion: It is extremely rare for NCPNS, UPNS, and IMPNS to occur concurrently. Surgical management for NCPNS and IMPNS, combined with conservative treatment for UPNS, may lead to favorable outcomes.
